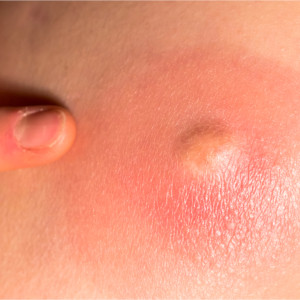
An abscess is an encapsulated collection of pus in the tissue of the human or animal body.
The triggers are usually bacteria such as staphylococci, streptococci or parasites and amoebas that invade the tissue.
A cavity forms where pus accumulates. The pus consists of dead tissue, dead immune cells and bacterial remains.
A distinction is made between cold and hot abscesses.
Cold and hot abscesses:
A hot abscess is caused by an acute infection.
Typical signs of inflammation appear at the affected site.
A cold abscess occurs due to a chronic infection such as tuberculosis. In comparison to the hot abscess, no acute inflammatory signs occur here.
Abscesses can form anywhere in the body. The skin (epidermis, dermis and subcutis) is most often affected because it is easily infected by pathogens. Abscesses can also develop as a result of a cut, an animal bite or as a result of invasive surgery.
People with a weakened immune system are more susceptible to an abscess.
In a healthy person, the immune system disposes of the dead body cells and pathogens.
In order for a boil to heal better, it must be opened and drained from the outside.
Abscesses must be treated with conventional medicine.
There is always a risk of sepsis.
Abscesses should never be opened by yourself. The abscess capsule can travel and the pus can empty into the inside.
The pathogens can enter the bloodstream and cause sepsis (blood poisoning).
CAFL:
| 2720 | 2170 | 880 | 787 | 727 | 190 | 500 |
Become a member now
As a member, you will receive further information and frequencies on this topic! Log in here!



