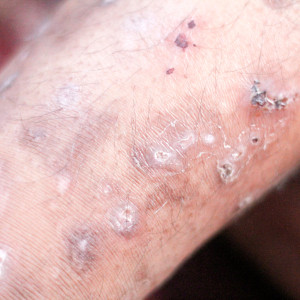
Acarodermatitis is a contagious and notifiable skin disease caused by mites.
In our country, this disease is better known as scabies.
Scabies mites are skin parasites, about 0.2 to 0.4 mm in size, and belong to the arachnid genus.
They mainly infest the warm areas of the upper skin layer of the body.
The mites feed on the cell fluid, lymph and skin cells of humans.
The parasites lay up to three eggs and faeces daily in the horny layer of the skin.
After a few days, the larvae hatch and migrate to the skin surface.
After about 2-3 weeks, the larvae develop into the sexually mature mites.
The life span of the females is between 30-60 days.
Outside the human body, they can survive at room temperature from 1-4 days.
Transmission occurs, among other things, through direct physical contact, as well as through sharing bed linen, towels, clothing, toys and the like.
The incubation period is days to weeks.
Most often, body parts such as:
- Wrists
- Interstices of fingers and toes
- Elbows
- Armpit region
- Knee
- Navel
- Groin and genital area
affected.
Typical symptoms are:
- severe itching (especially at night)
- small pustules
- visible mite entrances
- grey scaly skin inflammations
- scaly skin swellings
- scratched skin
The mites, their decaying bodies and their excretions trigger an allergic reaction in humans with a rash and severe itching. The itching causes sores, which in turn can be entry points for other infectious diseases, such as sexually transmitted infections.
Prophylaxis:
- avoid direct body contact
- good hygiene
- Change bedclothes and clothes daily and wash them at 60°C or more
- Vacuum carpets and furniture covered with fabric daily or have them dry-cleaned
Scabies must always be treated with conventional medicine and is notifiable in most European countries!
