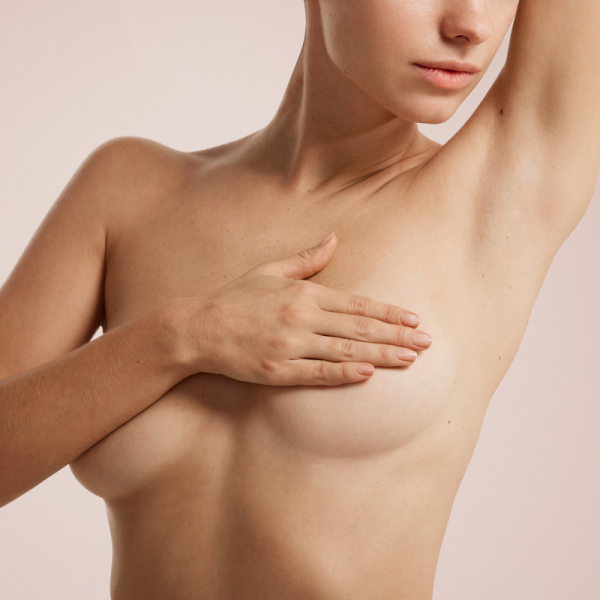
What is breast carcinoma?
Breast carcinoma is also colloquially called breast cancer and is the most common, although not the most dangerous, cancer in women. It is a malignant tumour in the mammary gland, which in rare cases can also affect men. In Germany, about 70,000 women get breast cancer every year, and the risk increases with age. If breast cancer is diagnosed and treated in time, for example during an early detection examination, the cancer can usually be cured.
What types of breast cancer are there?
Breast cancer can originate either in the cells of the lobules (lobular carcinoma) or in the cells of the milk ducts (ductal carcinoma). Ductal carcinoma is more common. It can also happen that the breast cancer is no longer limited to the breast alone and that tumour cells also form in the lymph node stations. The lymph nodes in the armpits are very often affected. More rarely, the lymph nodes behind and next to the breastbone are affected.
What contributes to the development of breast carcinoma?
So far, doctors have not been able to identify the actual causes of breast carcinoma. In the majority of patients, breast carcinoma occurs spontaneously, i.e. without any clear cause. However, there are the following risk factors that can favour the development of breast carcinoma:
- a hormonal imbalance, or hormone therapy: oestrogens, for example, can promote the development and multiplication of some cancer cells
- Smoking,
- incorrect eating habits, e.g. a diet too rich in fat: overweight women in particular are more likely to develop breast cancer than slim women, because hormones are produced in the fatty tissue that cause the oestrogen level to rise.
- high mammographic density: Women who have less fatty tissue but more glandular and connective tissue in their breasts have a fivefold increased risk of developing breast cancer.
- genetic predisposition: Women whose first-degree relatives have already developed breast cancer have a twofold increased risk of also developing breast cancer.
- Alcohol consumption,
- Obesity and type II diabetes,
- insufficient exercise,
- Irradiation of the chest in childhood, for example as a result of treatment for lymphoma
Furthermore, pregnancy and breastfeeding can also have an effect on the development of breast cancer. In addition, the time of the onset of the first menstrual period and the menopause can be decisive for the development of breast cancer.
What are the symptoms of breast cancer?
When breast cancer is in its early stages, the patient usually does not experience any symptoms. However, there are some signs that may indicate breast cancer. These include:
- Lumps or indurations in the breast,
- a sudden difference in the size of the breasts,
- bloody, watery and/or purulent discharge from one of the nipples,
- palpable lymph nodes, for example inside the armpit,
- different appearance of the breasts when the arms are raised,
- Discomfort in the breast area, such as a noticeable redness
In an advanced stage, the following symptoms may also occur:
- unwanted weight loss,
- general fatigue and frequent tiredness,
- general pain, such as pain in the limbs or back, which can be caused by metastases forming in the bones.
How is breast cancer diagnosed?
As with other cancers, the earlier the tumour is diagnosed, the better the chances of cure. If you suspect that you have breast cancer, you should see a doctor. The doctor will first take the patient's medical history and then examine her physically, especially feeling both breasts, but also the clavicle pits and the armpits.
If the physical examination is conspicuous, a mammography, i.e. an X-ray examination of the breast, is then carried out on patients over the age of 40. An additional ultrasound examination can increase the certainty of the diagnosis. If there is sufficient suspicion of breast cancer, a biopsy, i.e. a tissue sample, is performed. A laboratory test can determine whether the tumour is benign or malignant.
How is breast cancer treated?
The method of treatment always depends on the stage of the cancer, the size of the tumour and the patient's general state of health and whether the cancer has already metastasised. In most cases, the breast carcinoma is removed surgically, followed by radiotherapy to prevent the cancer cells from forming again.
If breast cancer is diagnosed at an early stage, it is possible to have breast-conserving surgery. If, on the other hand, the cancer is already more advanced, the entire breast is usually removed together with the lymph nodes from the armpit on the same side (radical surgery). The so-called follow-up therapies (adjuvant therapies) can consist of chemotherapy or anti-hormone therapy, for example. Depending on the size of the tumour, a combination of both procedures is also possible.
What rehabilitation measures can be carried out after a breast carcinoma?
After the surgical removal of a breast carcinoma, physiotherapy exercises can be helpful to regain freedom of movement and strength in the shoulder and the respective arm. If lymph nodes have been removed from the armpit, the arm on the operated side may swell. Lymphatic drainage can help with this.
Breast carcinoma frequencies
|
Pathogen |
Source |
Comment |
Frequencies |
|
Breast |
TTFields - Name of cell line: MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
|
Breast cancer 1 |
Use Blood Purification. |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
|
Breast Cancer 2 |
Use blood purification. |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
|
Breast Cancer 3 |
Use blood purification. |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after signing up. |
|
|
Breast Cancer 4 |
Use blood purification. |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after signing up. |
|
|
Breast Cancer 5 |
Use blood purification. |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
|
Breast Cancer |
EDTFL |
See also Cancer Sets. Use blood purification. |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after signing up. |
|
Breast Cancer |
EDTFL |
See also Cancer Sets. Use blood purification. |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after signing up. |
|
Breast Cancer 1 |
XTRA |
Use blood purification. |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
Breast Cancer 2 |
XTRA |
Use blood purification. |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
XTRA |
Use blood purification. |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
Frequencies Oncoviruses and Bacteria
Frequencies Epstein Barr Virus
|
Pathogen |
Source |
Frequencies |
|
Epstein Barr Virus |
BIO |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
EBV |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
|
Epstein Barr Virus 1 |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
|
Epstein Barr Virus 2 |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
|
Epstein Barr Virus Secondary |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
|
Epstein Barr Virus 1 |
HC |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
Epstein Barr Virus 2 |
HC |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
EBV |
VEGA |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
EBV 1 |
XTRA |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
EBV 2 |
XTRA |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
EBV 3 |
XTRA |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
EBV Secondary |
XTRA |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
Epstein Barr |
XTRA |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
Epstein Barr Virus 1 |
XTRA |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
Epstein Barr Virus 2 |
XTRA |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
Epstein Barr Virus 3 |
XTRA |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
Epstein Barr Virus 4 |
XTRA |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
Epstein Barr Virus 5 |
XTRA |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
Epstein Barr Virus 6 |
XTRA |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
Epstein Barr Virus 8 |
XTRA |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
Epstein Barr Virus 9 |
XTRA |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
Epstein Barr Virus A |
XTRA |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
Epsten Barr Virus B |
XTRA |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
Epstein Barr Virus Lyme |
XTRA |
Members receive access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
Human Herpes Virus - Type 6
|
Pathogen |
Source |
Frequencies |
|
HHV 6 |
XTRA |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
Herpes Type 6 1 |
XTRA |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
Herpes Type 6 2 |
XTRA |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
Herpes Type 6a |
XTRA |
Members receive access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
Frequencies human papilloma virus
|
Pathogen |
Source |
Frequencies |
|
Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) |
EDTFL |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
Papilloma |
EDTFL |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
Papillomavirus |
BIO |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
Papillomavirus |
PROV |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
Papilloma HPV 6a |
XTRA |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
Papilloma HPV 6b |
XTRA |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
Papilloma HPV 11 |
XTRA |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
Papilloma HPV 16 |
XTRA |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
Papilloma HPV 18 |
XTRA |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
Papilloma HPV 33 |
XTRA |
Members receive access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
Papillomavirus Infections |
EDTFL |
Members receive access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
Papilloma, Squamous Cell |
EDTFL |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) |
XTRA |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
Frequencies Bacteroides fragilis
|
Pathogen |
Source |
Frequencies |
|
Bacteroides fragilis |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
|
Bacteroides fragilis |
HC |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
Bacteroides fragilis 1 |
XTRA |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
Bacteroides fragilis 2 |
XTRA |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
Bacteroides fragilis 3 |
XTRA |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
|
Bacteroides fragilis 4 |
XTRA |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
Frequencies Detox
Frequencies Aluminium - Detoxification
|
Pathogen |
Source |
Frequencies |
|
Detox Aluminium |
XTRA |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
Use the following frequency sets in addition:
- Blood Purification
- Lymphatic system
- Cancer - Basis
