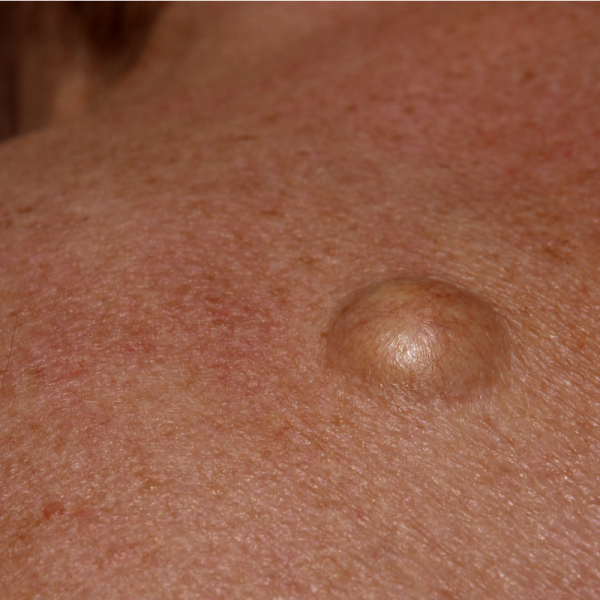
What is a sebaceous gland cyst?
A benign growth of the sebaceous gland is called a sebaceous gland cyst. Doctors also refer to this as an atheroma or a trichilemmal cyst. In common parlance, the sebaceous gland cyst is also called a groat pouch, because over time the contents of the cyst, the sebum, resembles groats in its consistency. In 90 percent of all cases, a sebaceous gland cyst develops on the hairy head and often occurs more frequently in this location. Sebaceous gland cysts can also form on the neck, abdomen, face and/or genitals.
How does a sebaceous gland cyst develop?
Sebaceous glands, which are found all over the skin, constantly produce sebum. This is an oily secretion that lubricates and softens the hair and skin. The sebum reaches the surface of the skin through a duct. If the duct is blocked, the sebum cannot get out and the sebaceous gland swells. As a result, a cyst develops.
Is a sebaceous gland cyst dangerous?
A sebaceous gland cyst is not dangerous, as long as the area is not inflamed. However, a sebaceous gland cyst looks unaesthetic, especially since it has appeared on a freely visible part of the body. If it is a sebaceous gland cyst on the scalp, it can cause discomfort when combing or sleeping.
How can a sebaceous gland cyst be diagnosed?
A sebaceous gland cyst usually grows up to 2 centimetres in size, but in very rare cases it can be the size of a chicken egg or a ping-pong ball. A typical feature of a sebaceous gland cyst is its hemispherical appearance and the bulging mass of sebum that can be pushed back and forth. The skin adjacent to a sebaceous gland cyst is keratinised. Since a sebaceous gland cyst can often be mistaken for an epidermoid cyst, a histological examination can be ordered in case of doubt.
How is a sebaceous gland cyst treated?
Since a sebaceous gland cyst is not a health concern in most cases, it does not necessarily need to be treated. However, because it grows steadily, a sebaceous gland cyst can become bothersome once it reaches a certain size. However, you should never try to push out the sebum yourself. This can lead to bacteria entering the sebaceous gland cyst and multiplying there. This can lead to inflammation. If the inflammation is not treated, it can also spread to the adjacent tissue, which makes the removal of the sebaceous gland cyst all the more difficult.
So if the cyst becomes bothersome, it is advisable to consult a doctor who can easily remove the sebaceous gland cyst surgically. To prevent a new cyst from forming over time, both the exit duct and the capsule are completely removed.
| Pathogen | Source | Members - Area |
|---|---|---|
| Cyst Sebaceous gland | EDTFL | As a NLS member you have direct access to these frequency lists |
| Cyst Sebaceous Gland | XTRA | As an NLS member you have direct access to these frequency lists |
| Cyst Sebaceous gland | XTRA | As a NLS member you have direct access to these frequency lists |
