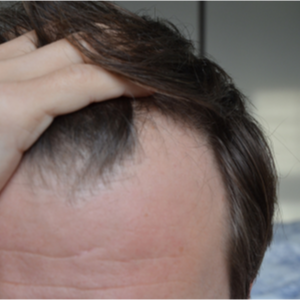
What is telogen effluvium?
Telogen effluvium is the sudden phenomenon of increased hair loss or thinning that occurs during the shedding process of the hair cycle. This occurs due to the hair cells entering a resting phase (telogen phase) at an early stage and occurs relatively frequently. Usually, telogen effluvium lasts up to six months and disappears on its own.
What can be the causes of telogen effluvium?
If the cell cycle of the hair cells changes, this can have the following causes:
- severe infectious disease associated with high fever, such as malaria,
- Anaemia,
- serious injuries,
- major surgery,
- emotional and physical stress over a long period of time,
- Fasting and/or dieting over a long period of time, during which the body is deprived of important nutrients (including iron),
- Heavy metal poisoning,
- Allergy(s),
- pregnancy, but also childbirth can trigger so-called postpartum hair loss,
- Side effects of medication (especially cytostatics),
- Hormone disorders (especially hyper- or hypothyroidism),
Telogen effluvium is not hereditary. So even if one family member has telogen effluvium, this does not necessarily mean that other family members will also be affected.
How does telogen effluvium develop?
Hair growth occurs based on the following cyclical changes in the activity of the hair follicles:
- Growth phase (anagen): lasts for about 3 to 7 years triggers hair growth. Most hair follicles exist in the growth phase.
- Transition phase (catagen): lasts only up to 3 weeks and serves the maintenance phase of the hair.
- Resting phase (telogen): lasts between 2 and 4 months and ends when the hair is shed. People who suffer from telogen effluvium have a significantly increased proportion of follicles located in telogen, which leads to increased hair loss.
If telogen effluvium lasts longer than six months, doctors call it chronic telogen effluvium, which is rare.
What is the difference between telogen effluvium and anagen effluvium?
While telogen effluvium occurs during the shedding phase of the hair cycle and manifests as sudden severe hair loss about three months after the triggering event, anagen effluvium occurs during the growth phase of the hair growth cycle and manifests only a few days after the triggering event. While telogen effluvium can have numerous motives, the most common cause of anagen effluvium is chemotherapy treatment.
What are the symptoms of telogen effluvium?
Telogen effluvium is mainly manifested by scarless hair loss. In addition, women in particular tend to lose their hair when brushing. Doctors call this diffuse hair loss and thus distinguish telogen effluvium from other types of hair loss, such as androgenic alopecia, in which so-called receding hairline or thinning of the hair crown occurs.
People who suffer from telogen effluvium usually have the sensation of sudden very severe hair loss from tufts of hair found in the shower drain or hairbrush, for example. This experience can be very traumatic in some circumstances.
How can telogen effluvium be prevented?
Stress can promote and trigger sudden severe hair loss. To prevent telogen effluvium, stress should be avoided. Various stress management techniques can be used, such as meditation or getting enough sleep. In addition, it is of course important to eat a nutritious diet. This includes wholemeal products, healthy fats, lean protein and sufficient fruit and vegetables. Additional food supplements for the hair also ensure that the hair receives all the important nutrients it needs to grow back.
Cosmetically, a haircut can help to conceal telogen effluvium. Not only does shorter hair usually look more voluminous, but cutting off split ends can prevent hair breakage. Since frequent hair colouring and heat styling have also been proven to contribute to hair breakage, curling irons, straightening irons and hair dryers should be avoided. If you do not want to do without them, heat protection products such as Hair Strengthening & Protection Oil can help.
How is telogen effluvium diagnosed?
The dermatologist usually makes the diagnosis of telogen effluvium. To do this, he or she will usually first rule out other forms of hair loss, such as circular hair loss (alopecia areata). It is also important to determine the causes of the hair loss.
How is telogen effluvium treated?
The treatment method always depends on the underlying disease. Accordingly, drug treatment with the following agents is possible.
- Iron substitution, for example, to prevent diffuse effluvium,
- Thyroid hormones,
- Food supplements such as amino acids, trace elements and/or vitamins
